Core Concept and Operating Principles
At a fundamental level, a Cylindrical capacitor stores electrical energy in an electric field formed between conductive electrodes separated by a dielectric material. When integrated into AC power systems, Capacitors are primarily used to compensate for inductive loads, improve power factor, reduce line losses, and stabilize voltage.
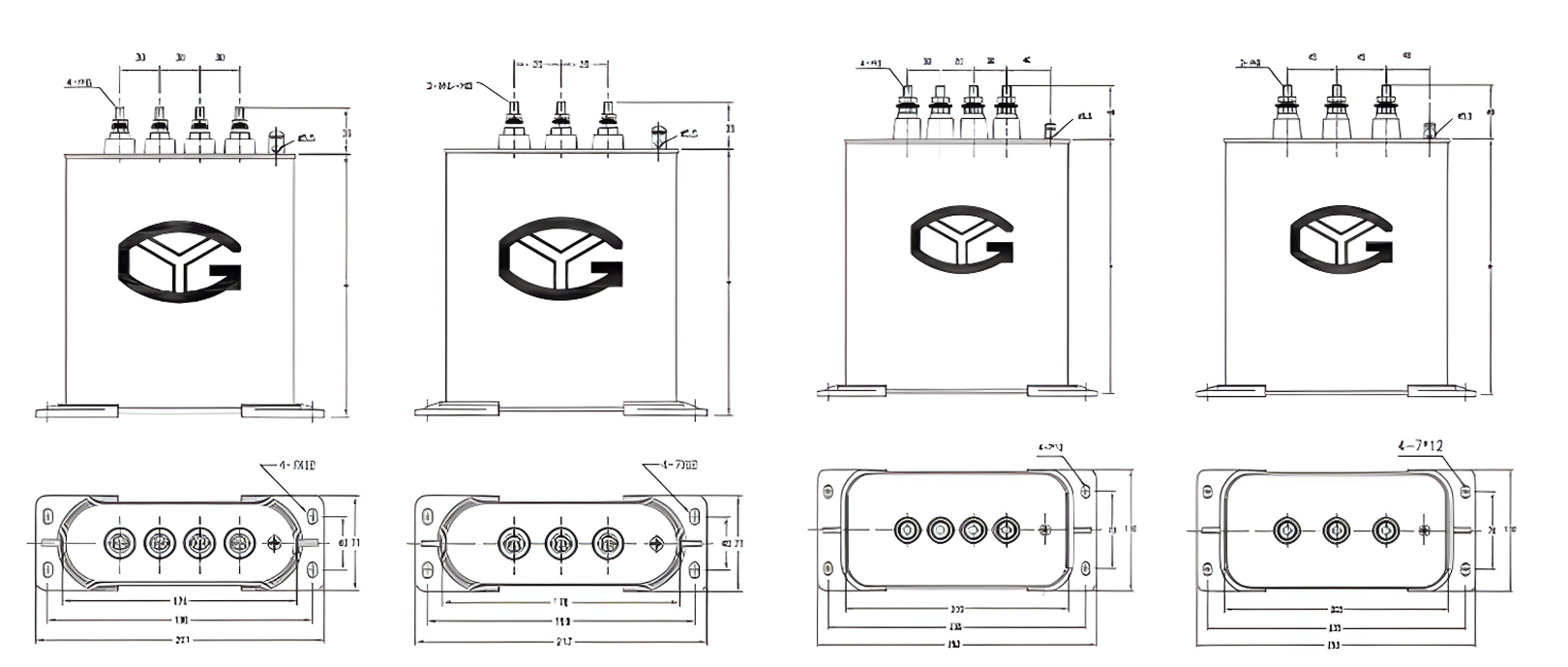
The cylindrical form factor is not merely a packaging choice. Compared with rectangular or box-type designs, cylindrical capacitors offer more uniform mechanical stress distribution and predictable heat dissipation paths. This geometry supports higher operational stability under continuous load, especially in environments with elevated ambient temperatures or frequent load fluctuations.
In power compensation systems, these capacitors are typically connected in parallel with inductive equipment, supplying reactive power locally and reducing the burden on upstream power infrastructure.
Product Structure, Materials, and Manufacturing Processes
A typical cylindrical capacitor consists of several key structural elements, each influencing performance and service life.
Shell and Surface Treatment
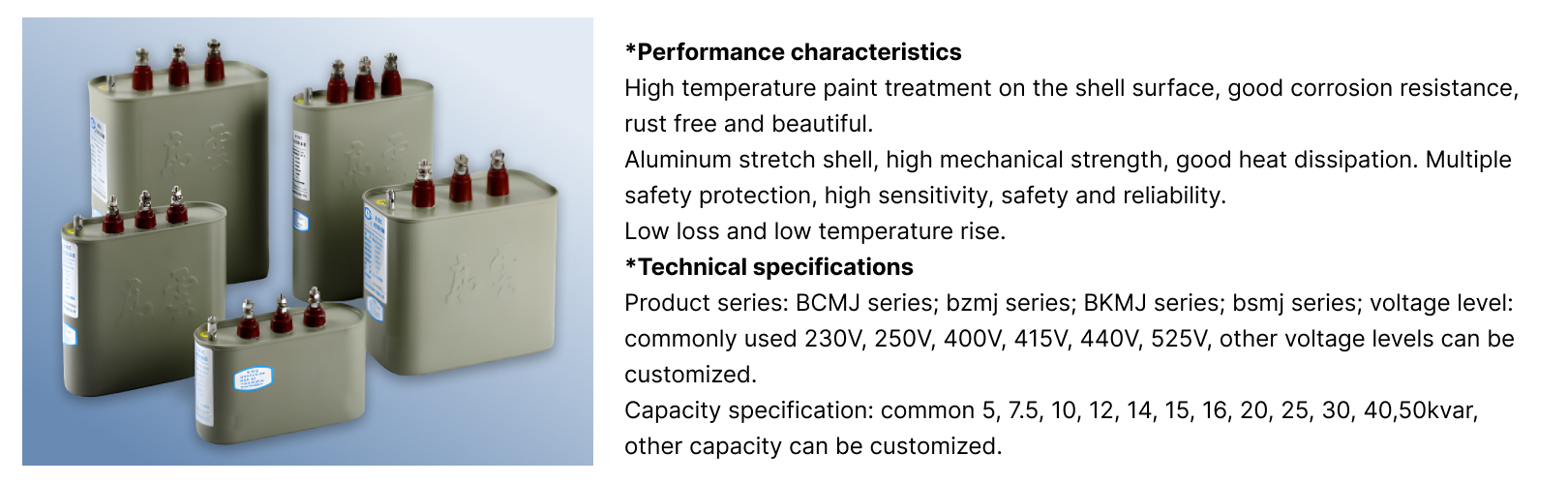
The outer shell is commonly manufactured using an aluminum stretch-forming process. Aluminum provides a balance of mechanical strength, low weight, and thermal conductivity. High-temperature paint treatment applied to the shell surface enhances corrosion resistance, prevents rust formation, and maintains long-term aesthetic and functional integrity in industrial environments.
This surface treatment is particularly important in applications exposed to humidity, dust, or mild chemical atmospheres, such as manufacturing plants or utility rooms.
Dielectric System and Internal Construction
Inside the shell, metallized dielectric films are wound or stacked with precision to achieve the required capacitance and voltage rating. Low-loss dielectric materials are selected to minimize internal heat generation and ensure low temperature rise during operation.
Resin or environmentally compliant filling compounds are often used to stabilize the internal structure, improve insulation, and eliminate leakage risks. These materials also contribute to vibration resistance and long-term reliability.
Electrical Characteristics
Modern cylindrical capacitors are designed for low loss and high thermal stability. Reduced dielectric loss directly translates to lower operating temperatures, which is one of the most critical factors affecting capacitor lifespan. Multiple internal safety mechanisms, such as overpressure disconnection or self-healing metallization, are incorporated to ensure predictable failure modes and system safety.
Key Factors Influencing Quality and Performance
Several engineering and manufacturing factors determine the real-world performance of a cylindrical capacitor:
Thermal Management
Effective heat dissipation depends on shell material, surface finish, and internal layout. Aluminum shells with optimized wall thickness and smooth thermal paths significantly reduce hotspot formation.
Voltage Margin and Dielectric Integrity
Operating a capacitor close to its rated voltage accelerates dielectric aging. Designs that allow stable operation across commonly used voltage levels—such as 230V, 400V, or 440V—provide better reliability in fluctuating grid conditions.
Capacitance Stability
High-quality dielectric films and precise winding processes ensure that capacitance remains within tolerance over time, even under temperature cycling.
Manufacturing Consistency
Automated winding, controlled curing processes, and end-of-line testing reduce unit-to-unit variation, which is essential for multi-capacitor banks.
Voltage and Capacity Configurations
Cylindrical capacitors are produced in a wide range of voltage and capacity specifications to match diverse system requirements. Common voltage levels include 230V, 250V, 400V, 415V, 440V, and 525V, allowing integration into both single-phase and three-phase power systems.
Capacitance values typically range from smaller units such as 5 or 7.5 kvar to larger ratings up to 50 kvar. Modular capacity options enable engineers to scale compensation systems incrementally, improving flexibility in design and maintenance. Custom voltage or capacity configurations may be required for specialized equipment or regional grid standards.
Supply Chain and Supplier Selection Considerations
Selecting a cylindrical capacitor supplier is not solely a matter of price. For industrial and infrastructure projects, long-term reliability and technical support are often more critical.
Key evaluation criteria include:
Engineering Documentation and Traceability
Suppliers should provide clear technical specifications, test data, and compliance information.
Process Control and Quality Systems
Consistent production quality is usually supported by standardized manufacturing processes and documented quality management systems.
Application Support
Technical guidance on derating, environmental conditions, and system integration can significantly reduce field failures.
Lifecycle Availability
For long-lived equipment, component continuity and backward compatibility are essential.
Common Industry Challenges and Pain Points
Despite their mature technology, cylindrical capacitors are not immune to misuse or misapplication. Common challenges include premature aging due to thermal overload, incorrect voltage selection, and inadequate ventilation within capacitor banks.
Another frequent issue is underestimating environmental stress factors such as ambient temperature, harmonics, or mechanical vibration. In installations with high harmonic distortion, standard capacitor designs may experience elevated losses, emphasizing the need for proper system analysis during the design phase.
Application Scenarios and Industry Use Cases
Cylindrical capacitors are widely deployed across multiple sectors:
Industrial Motors and Pumps
Used for power factor correction to reduce energy losses and stabilize motor operation.
HVAC and Air Conditioning Systems
Improve efficiency and reduce reactive power demand in commercial buildings.
Elevators and Lifting Equipment
Provide consistent reactive power support during frequent start-stop cycles.
Manufacturing Machinery
Support stable voltage conditions in printing, textile, and automation equipment.
In each of these applications, reliability under continuous operation and compact form factors are decisive advantages.
Trends and Future Development Directions
The future of cylindrical capacitor technology is shaped by higher efficiency requirements, compact system design, and sustainability considerations. Ongoing developments focus on lower-loss dielectric materials, improved thermal modeling, and enhanced safety mechanisms.
Digital monitoring and smart capacitor systems are also emerging, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time performance tracking. As electrical systems become more data-driven, capacitors will increasingly be viewed not as static components, but as integrated elements within intelligent power networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What distinguishes a cylindrical capacitor from other form factors?
Its geometry supports uniform stress distribution, efficient heat dissipation, and robust mechanical performance.
How does temperature affect capacitor lifespan?
Higher operating temperatures accelerate dielectric aging; low-loss designs with effective heat dissipation significantly extend service life.
Can cylindrical capacitors be customized?
Yes, voltage levels and capacitance values can be adapted to specific system requirements, subject to engineering validation.
Conclusion
Cylindrical capacitors remain a foundational component in modern power systems, valued for their structural reliability, thermal performance, and adaptability across industries. Understanding their design principles, performance drivers, and application contexts enables engineers and system designers to make informed decisions that improve efficiency, reliability, and long-term operational stability.

 English
English
 Español
Español
 Portugues
Portugues
 Pусский
Pусский
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 日本語
日本語
 한국어
한국어
 العربية
العربية
 Italiano
Italiano
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 Svenska
Svenska
 Polski
Polski
 Türk dili
Türk dili
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Melayu
Melayu
 dansk
dansk
 Magyar
Magyar
 বাংলা
বাংলা
 עִברִית
עִברִית
 čeština
čeština
 українська
українська
 беларускі
беларускі
 Filipino
Filipino
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
 اردو
اردو
 հայերեն
հայերեն
 български
български
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
 galego
galego
 नेपाल
नेपाल
 euskara
euskara
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
 Malagasy
Malagasy
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
 Ilocano
Ilocano
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн
















 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Телефон
Телефон